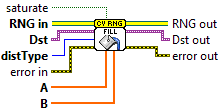
Fill
OpenLvVision_OpenCv.lvlib:RNG.lvclass:RNG Fill.vim
Fills arrays with random numbers.
Each of the methods fills the matrix with the random values from the specified distribution. As the new numbers are generated, the RNG state is updated accordingly. In case of multiple-channel images, every channel is filled independently, which means that RNG cannot generate samples from the multi-dimensional Gaussian distribution with non-diagonal covariance matrix directly. To do that, the method generates samples from multi-dimensional standard Gaussian distribution with zero mean and identity covariation matrix, and then transforms them using transform to get samples from the specified Gaussian distribution.
For detailed information, please refer to the OpenCV documentation
| error in error in can accept error information wired from VIs previously called. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| status status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| code |
| source source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| saturate |
| Dst 2D or N-dimensional array or image currently matrices with more than 4 channels are not supported by the methods, use Mat::reshape as a possible workaround. |
| A first distribution parameter; in case of the uniform distribution, this is an inclusive lower boundary, in case of the normal distribution, this is a mean value. Every element gets mapped to an channel: 0 = Blue/Real 1 = Green / Imaginary 2 = Red 3= Alpha |
| Numeric |
| B Second distribution parameter; in case of the uniform distribution, this is a non-inclusive upper boundary, in case of the normal distribution, this is a standard deviation (diagonal of the standard deviation matrix or the full standard deviation matrix). Every element gets mapped to an channel: 0 = Blue/Real 1 = Green / Imaginary 2 = Red 3= Alpha |
| Numeric |
| RNG in Object by reference! Random number generator. It encapsulates the state (currently, a 64-bit integer) and has methods to return scalar random values and to fill arrays with random values. |
| distType Distribution type 0 = UNIFORM 1 = NORMAL. |
| error out error in can accept error information wired from VIs previously called. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| status status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| code |
| source source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| Dst out 2D or N-dimensional array or image currently matrices with more than 4 channels are not supported by the methods, use Mat::reshape as a possible workaround. |
| RNG out Object by reference! Random number generator. It encapsulates the state (currently, a 64-bit integer) and has methods to return scalar random values and to fill arrays with random values. |