Invert
OpenLvVision_OpenCv.lvlib:Invert.vim
Finds the inverse or pseudo-inverse of a matrix.
The function cv::invert inverts the matrix src and stores the result in dst . When the matrix src is singular or non-square, the function calculates the pseudo-inverse matrix (the dst matrix) so that norm(src*dst - I) is minimal, where I is an identity matrix.
In case of the DECOMP_LU method, the function returns non-zero value if the inverse has been successfully calculated and 0 if src is singular.
In case of the DECOMP_SVD method, the function returns the inverse condition number of src (the ratio of the smallest singular value to the largest singular value) and 0 if src is singular. The SVD method calculates a pseudo-inverse matrix if src is singular.
Similarly to DECOMP_LU, the method DECOMP_CHOLESKY works only with non-singular square matrices that should also be symmetrical and positively defined. In this case, the function stores the inverted matrix in dst and returns non-zero. Otherwise, it returns 0.
For detailed information, please refer to the OpenCV documentation
| error in error in can accept error information wired from VIs previously called. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| status status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| code |
| source source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
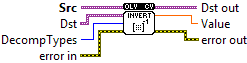
| Src input floating-point M x N matrix. |
| Dst The output matrix dst maintains the same data type as the source. However, when specifying the DECOMP_SVD flag, the function resizes dst to swap the input's row and column counts. In this specific configuration, providing the dst is mandatory |
| DecompTypes DECOMP_LU: Gaussian elimination with the optimal pivot element chosen. DECOMP_SVD : singular value decomposition (SVD) method; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix DECOMP_EIG: eigenvalue decomposition; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical DECOMP_CHOLESKY: Cholesky factorization. he matrix src1 must be symmetrical and positively defined. DECOMP_QR: QR factorization; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular DECOMP_NORMAL:while all the previous flags are mutually exclusive, this flag can be used together with any of the previous; it means that the normal equations |
| error out error in can accept error information wired from VIs previously called. Use this information to decide if any functionality should be bypassed in the event of errors from other VIs. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| status status is TRUE (X) if an error occurred or FALSE (checkmark) to indicate a warning or that no error occurred. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| code |
| source source describes the origin of the error or warning. Right-click the error in control on the front panel and select Explain Error or Explain Warning from the shortcut menu for more information about the error. |
| Dst out |
| Value |